Introduction
As we shared in Part 1, the future of Pharma and Biotech is possible because of new tools and technologies, along with all clinical discoveries and relevant data that has accumulated throughout the years. In that blog, we learned about the technology drivers behind the Biotech processes and the collaborative strategies accelerating changes, facilitating dynamic response and the globalization of markets.
Knowing of the significant growth in Pharma, Biotech, Medical Devices, among other applications, this rapid and dynamic growth requires sophisticated technology. The future is in continuous evolution — and time moves fast when aiming to meet market demands. Technology is a key factor to rapidly transform operational processes to meet this demand.
Innovative technology is changing the world in the life sciences space. As the COVID-19 outbreak began, companies were forced to invest in digital innovations, bringing a radical transformation in Pharma/Biotech operations. Companies in these industries are under increased pressure to fast-track innovation to improve their operations to adapt new approaches, such as “Industry 4.0”, (also known as “Bioprocessing 4.0” in the Biotech world, or Pharma 4.0 in pharmaceutical applications).
But what do these innovative transformations mean for cultural change? Well, have you ever heard about the term “Agile”? And do Agile concepts help to transform company cultures? Agile and digitalization are two of the concepts to compact the growing and intense competition. These are efforts to keep up with the increased demand of personalized medicine and therapies.
In this blog post, we’ll find out more about technology transformations, as well as the road map to implementing radical change in the Pharma/Biotech world, toward a very promising future.
Digital Solutions
Biopharmaceutical Companies
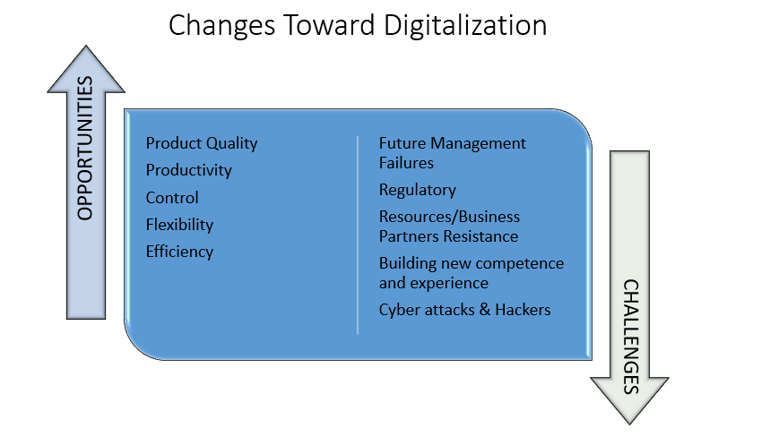
Digital technologies are changing the world market, not only in the life sciences space but in many other industries: aviation, telecommunications and film, to name a few. We are entering an era where biopharma innovation is moving at a pace that outstrips the life of a patient. Those companies that cannot innovate fast enough will face difficulties, ultimately falling behind their competition.
Figure 1: Potential challenges in the face of innovation
Future Technology that Exists Already
Did you know that hologram TV and wireless electric transmission already exists? Mankind has already given shape to these amazing futuristic ideas and invented extraordinary things.
Let’s take a look at a few of them in the scientific world:
- Printing of human organs: 3D bio-printers have the ability to grow arteries, and complex body parts like heart, teeth and bones will be able to be grown in next 7 – 10 years (or less).
- Synthetic Chemistry: Pharmaceuticals produce medicines from chemicals and/or synthetic process. This has been an important breakthrough to accelerate new drug discovery, and to produce therapies to address global health needs. It is not limited to breakthroughs in protein engineering, as molecular biology and bioinformatics are accelerating new drug discoveries.
- A capsule that could replace injections: The capsule is swallowed, reaches the intestine, dissolves and starts the delivery mechanism using a micro needle into the intestinal wall. The drug is absorbed like subcutaneous injection. What a tremendous breakthrough! Commercialization is near, and the drug will be covering most compromising conditions like Chron’s disease, hemophilia, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, growth hormone deficiencies and psoriasis arthritis. This is an exciting innovation with high bioavailability, like a subcutaneous injection with several molecules.
- Soft Skin Patch: A soft and stretchy ultrasound patch that can be worn on the skin to monitor blood flow through major arteries and veins deep inside a person’s body. This non-invasive patch can sense and measure cardiovascular signals as deep as 14 centimeters inside the body.
There is more new technology in the pipeline, in addition to a large amount of research and development focused on future innovations in the life sciences field.
Industry 4.0 in the life sciences field contributes toward an intelligent automation technology, and may support the increase of manufacturing operations focused on personalized medicine, additive manufacturing, localized 3D, printing of treatments, and more. Digital technology is more important than ever after COVID-19 sped up improvements in manufacturing productivity, competitive skills, planning and forecasting, and financial sustainability.
Industry 4.0 is the digital transformation of manufacturing/production and related industries and the value creation process. Manufacturers are integrating new technologies, including internet of things (IoT), cloud computing, analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and machine learning into their production facilities and throughout their operations. 3D, which is part of industry 4.0 is a form of additive manufacturing. Companies like Adidas use 3D printing for the creation of their shoe designs based on big data, another real-world example of Industry 4.0 being used by businesses today. Refer to figure 2.0 for the Industry evolution from 1.0 to 4.0.
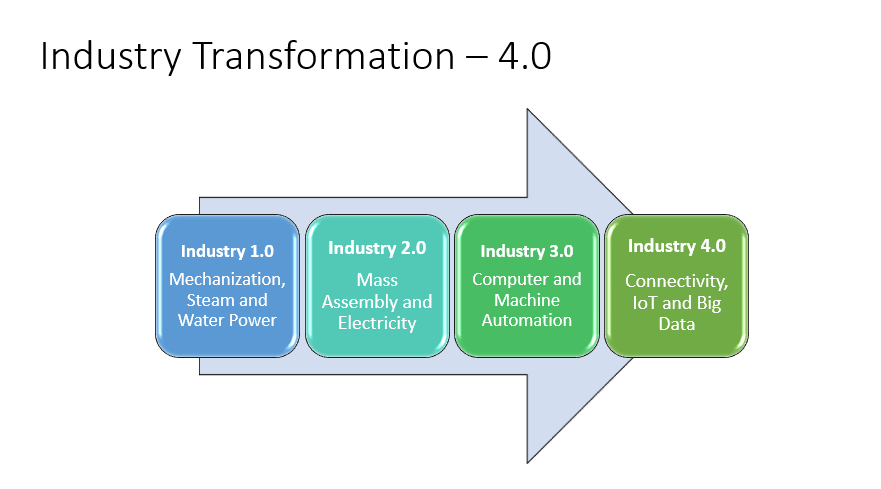
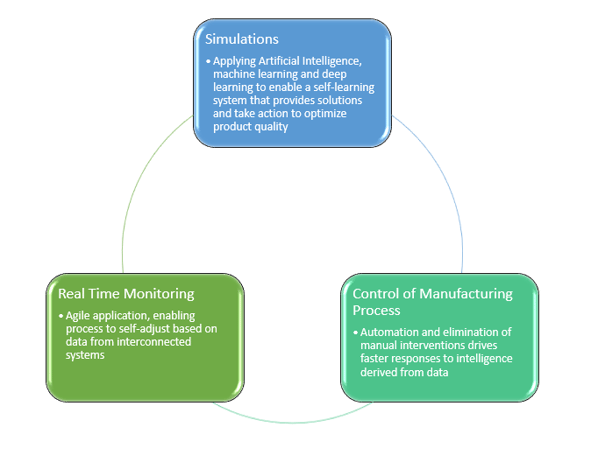
Figures 2&3: Industry 4.0 transformation process
Four important points summarizing Industry 4.0 are:
- Interconnection — the ability of machines, devices, sensors, and people to connect and communicate with each other via the Internet of things, (IoT) or the internet of people (IoP).
- Information transparency — the transparency afforded by Industry 4.0 technology provides operators with comprehensive information to make decisions. Inter-connectivity allows operators to collect immense amounts of data and information from all points in the manufacturing process, identifying key areas that can benefit from improvement to increase functionality.
- Technical assistance — the technological facility of systems to assist humans in decision-making and problem-solving, and the ability to help humans with difficult or unsafe tasks.
- Decentralized decisions — the ability of cyber physical systems to make decisions on their own and to perform their tasks as autonomously as possible. Only in the case of exceptions, interference, or conflicting goals, are tasks delegated to a higher level.
On another post we will expand more about this interesting topic and discuss the challenges that CDMO and CMO industries are facing toward this digital transformation.
Agile Transformation
Innovation and digitalization force a change in culture. There should be a complete transformation within the organization regarding resources. By following some innovative tools, an organization can predict and effectively provide transparency in their processes using the right technology and empowering their resources. Organizations must get rid of the “old way” or traditional process, otherwise it is not possible to implement innovations throughout digital transformation.
You may hear about the term Agile, an approach that breaks down the traditional method into short bursts or sprints, producing deliverables each time. In addition, agile involves regular retrospectives evaluating how things could have gone better, continued focus on customer needs and how they might change during the project, preventing things that won’t add value to the project, and meetings where each member gets together to mitigate issues. There are no established structures; teams are formed based on project needs, with product owners continuously assessing customer needs and reprioritizing if necessary. As a result, team members are empowered to compete the tasks. However, there is a lot of experimentation with an implicit understanding that perfection is not the end goal. Teams using Agile methods get things done faster than teams using traditional processes. They keep customers happier and enjoy their work more.
Agile provides a set of methods and practices where solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organizing, cross-functional teams. There are software/programs that have been developed to facilitate faster and smoother processes in multiple applications in the life sciences areas. Having technology be more accessible to resources will enhance the productivity interfacing with computers and software, which will allow teams to maximize the results of the process.
Digitalization
With a growing population and continuous world changes, digitalization is crucial to continue delivering medical products centered around patient needs. Good Manufacturing Practices, or GMP’s, are critical and need to be part of the digital transformation. Still, regulated organizations face many challenges, and deviations from these standards could severely impact patient health and government. There are five GMP principles within the major compliance areas to ensure quality consistency, safety, and efficacy of the products:
- People
- Procedures
- Process
- Facilities/Equipment
- Products
Implementing digitalization can improve quality control efficiency and reliability. During the production process, initial results are available. As soon as the batch is completed, all reports and compliance documentation are ready, all thanks to digitization technology. We all know that pharmaceutical firms are subject to rigorous rules and standards and the integrity of the data is critical. The use of digitization helps to monitor, regulate, and optimize production processes, increasing efficiency and productivity. New business models in the bio-pharma space such as CDMO differ from the traditional drug manufacturing industry. CDMO is a completed operation from drug development and manufacturing, and works directly with clients who sometimes want to outsource specific parts of their process. This operation goes through development, stability studies, Phase I and last stage of clinical trials, scale up, commercial production and shipment. Digitization-GMP development and implementation in the CDMO will be easier in comparison with the traditional operation, due to a lower risk during new product manufacturing, expertise, technology, and higher investment competence.
EGLS integrates services and provides strategic innovative solutions to our partners adding value to their operations. We assess, correct/develop, and implement to scale for operational optimization through technology and Agile, providing predictability and transparency through the process.
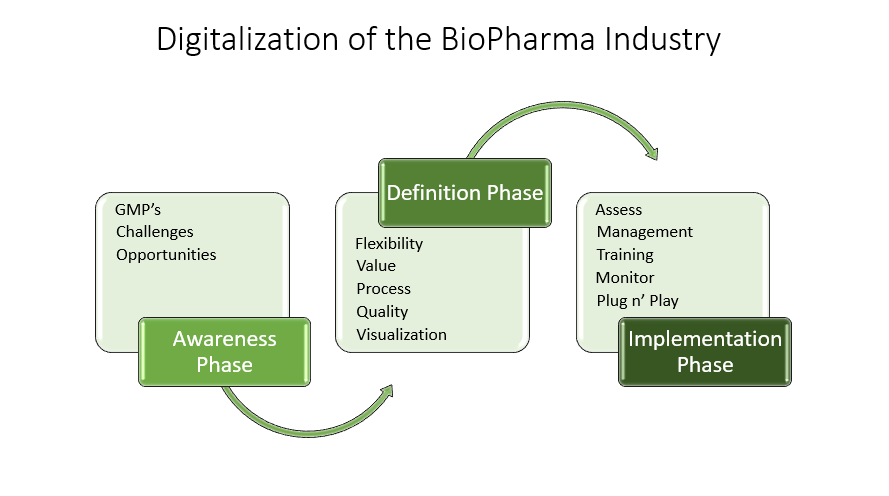
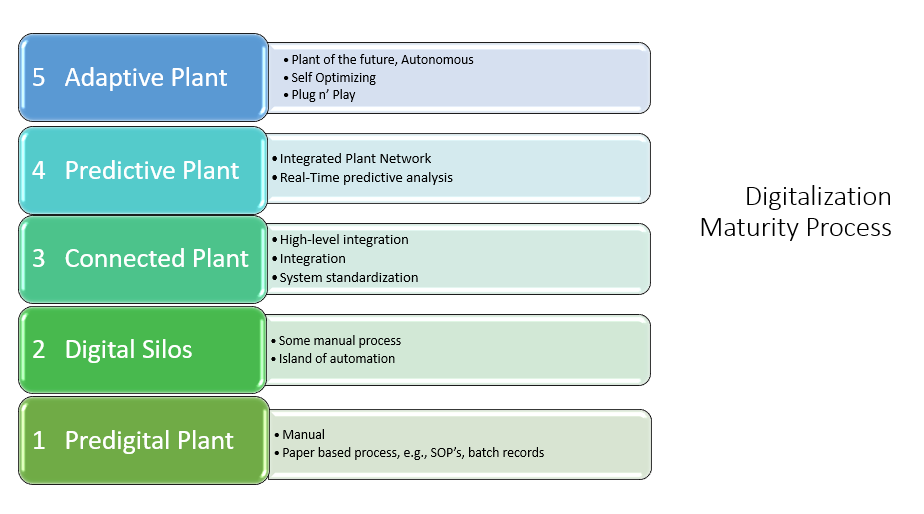
Figures 4,5&6: Digitalization within Biopharma
Summary
Just before the COVID-19 outbreak, the BioPharma industry was adopting digital technology at a slower pace than other industries, however there was an inflection point where innovative digital technology acceleration was forced by the outbreak. Now, digital transformation is essential and needed more than ever. Several organizations are moving fast to develop and implement digital concepts, not limited to resources, cultural changes, and adopting Agile concepts. These need to be synchronized to create a full change within the operation, with the required expertise and education.
From molecule, to market, to innovating, R&D and the cloud are all driven by digitization. Instead of using a notebook, most companies have implemented the use of tablets. Most data is reviewed while the manufacturing process is running. Through digital patient monitoring, the IoT (Internet of Things), and wearables, clinicians can monitor patient health indicators that automatically highlights signs of risk, and there is more to come in the digital future.
Digital transformation is important and necessary — not only to increase productivity, but to quickly respond to our population’s health demands. As time goes on, industries and businesses from all sectors will be forced to adopt digital applications.
Learn more about how EGLS can help your company keep up!

LINKS/REFERENCES
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aat0805
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-biotechnology-market
- https://www.ich.org/page/process-harmonisation
- https://phil.cdc.gov/group_researchers.aspx


